Wondering what latency means, and how you can reduce it?
In this guide, we’ve explained broadband latency. We’ve discussed what latency actually is, what happens if you have high latency, and how you can improve your latency with a few easy steps.
What is broadband latency?
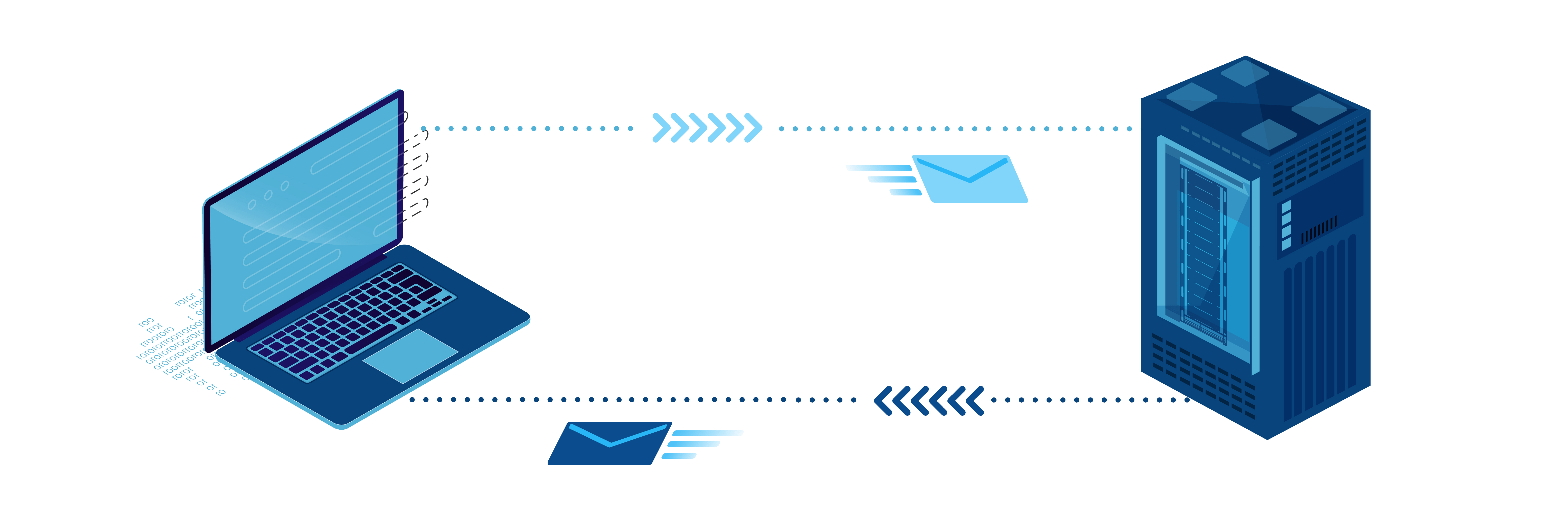
In broadband terminology, the word latency refers to how long it takes a request to travel from your device to another device over the internet.
When you do something online, you make a request to another computer, basically saying “I would like this data, please”.
If all goes well, you receive a response from the computer you make the request to, saying “Sure, let me begin sending you the data you need”.
Your latency (also known as “ping”) measures the time it takes for the entire journey from when you make a request, to receiving a response.
Let’s look at a simplified example of how computers communicate over the internet, from when you loaded this article you’re reading right now.
- Your computer, phone, or tablet made a request to the Broadband Savvy web server. A server is a type of computer that serves requests from other devices.
- The Broadband Savvy web server acknowledges the request, sending a message back to your computer.
- The Broadband Savvy web server sends the web page data, and the web page begins loading on your device.
Latency measures how long it takes to complete steps one and two. This is the time taken for your request to travel from your device, to your router (or the 4G/5G network), to your internet service provider, to our server, and finally back to you.

Latency does not measure broadband speeds. In step three, when the page begins downloading, the speed at which this occurs is instead measured by your broadband speed, rather than your ping.
Latency is measured in milliseconds, and the lower the latency you have, the better.
What is a good latency?
A good latency is less than 50 milliseconds, when measured using a nearby server (ideally in the same country).
If you make a request to a server on the other side of the world, it’s normal for it to take 200 milliseconds to come back, even if you have a good broadband connection.
A latency of 20ms or less is considered very good. With a ping rate this low, your latency is barely noticeable.
How to test your latency
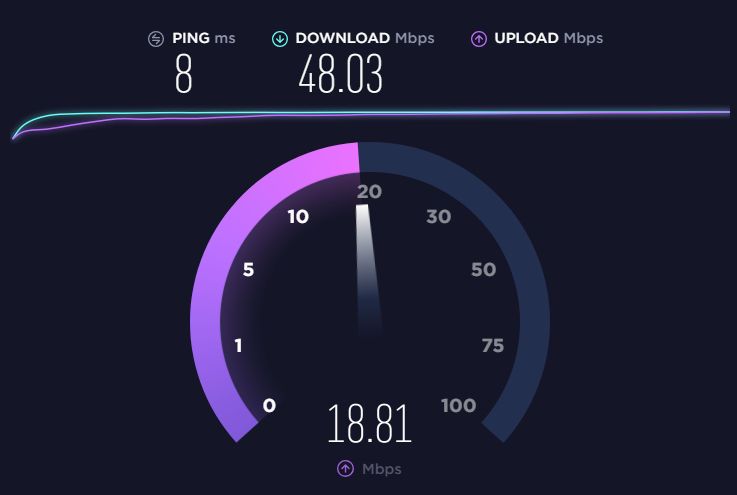
To test your ping, you can use a website called speedtest.net. This service will ensure to use a local server, to give you an accurate latency reading.
Simply navigate to the website, and hit the big “Go” button. Your latency, download speed, and upload speed will be displayed after the test is complete.
What does it mean if you have high latency?
As we mentioned above, having a low latency means that your ping is less than 50 milliseconds. However, it’s entirely possible to have a latency of 100, 200, or 300 milliseconds, and barely notice it.
If you have a high latency, you may experience a slight delay when performing tasks over the internet. For example, when you load a website, or send an email.
However, the main effect of a high latency is how it creates lag when online gaming, or a delay when using video calling apps, such as Zoom.
When playing games online, your computer is in constant communication with the game server. Your device lets the server know where your player is located, and what you’re doing. Likewise, the server lets you know where other players are located, and what they’re doing.
If you have a high ping when gaming, these updates cannot occur fast enough. As a result, you will experience significant amounts of lag. This could result in the game feeling slow, delayed inputs, or players jumping around the screen.
Likewise, when video calling, data is constantly being transferred between each device, and these transmissions must occur in real-time. The software cannot buffer video or voice data, like when you watch YouTube, because it has to be played live. Therefore, you might experience stuttering if using Zoom, Facetime or Microsoft Teams on a high latency connection.
Latency vs broadband speed
While latency measures the time it takes to send and receive small requests, broadband speed measures the time it takes to download or upload larger amounts of data.
Latency is the most important measure for gaming and live calls, while your speeds (also known as bandwidth) are what matter most when streaming videos, downloading large media files, or browsing social media.
- If you have a high ping and a fast download speed, you will experience a slight delay when initiating a request, but fast downloads once the initial request has gone through. You will experience lag when playing video games.
- If you have a low ping and slow speeds, most online activities will feel fine, as long as they are not data-intensive. For example, gaming will be smooth, and basic websites will load relatively quickly. However, large downloads will take a long time, and you may experience buffering when video streaming.
What causes high latency?
There are a number of different reasons you might have high latency.
- Your bandwidth is being used up. If lots of people are using your broadband connection, to the point where all of your bandwidth is used up, then even small requests will slow to a crawl, sending your latency skyrocketing. This is especially likely to happen when you have relatively slow broadband, and lots of people begin using the internet at once. To find out whether you have enough bandwidth, you can use this tool to calculate your broadband speed needs.
- You’re attempting to communicate with a server on the other side of the planet. This is why, even with a perfect internet connection, you will still lag when gaming on game servers hosted in far away locations.
- You’re using Wi-Fi, and your signal isn’t the best. In this case, you can improve response times, and reduce latency, by using a wired rather than a wireless connection to your router. Meaning, plugging your computer into your router using an Ethernet cable could make a significant difference to your ping.
- You’re using a VPN. Since the traffic has to travel through the VPN provider, this adds a delay, increasing your latency.
- You’re using mobile broadband to connect to the internet. While 4G and 5G services especially are often very fast, they can have a less consistent ping, depending on the quality of the mobile network in your area.
- You’re using satellite broadband. Since your connection has to travel all the way up to a satellite, down to Earth again, to the server, and then back again, satellite broadband providers often have a very high latency.
- You have a poor fixed-line broadband connection. In general, having slow broadband, such as an ADSL connection, shouldn’t affect your latency directly. However, if you rely on old network infrastructure, your connection is more likely to be inconsistent, which can cause ping spikes.
How to reduce broadband latency
There are a number of ways you can get a lower latency and reduce the lag or delay you experience when using the internet.
Here are a few different methods to reduce your broadband latency. We have listed the methods in the order we would try them, assuming each method is applicable to your situation.
- When gaming, ensure to connect to game servers located near to you.
- Plug your device into your router directly, using an Ethernet cable. If the two are too far apart, use a powerline adapter to send the signal through your electricity cables, and avoid having to run a line directly between the two devices. See the video we’ve embedded below this list to learn more about setting up a powerline adapter.
- Restart your router. If it’s been a while, it could be that this is causing network issues, resulting in a high latency. To restart your router, unplug the device, leave it unplugged for 10 minutes, plug it back in again, and wait another 5 minutes for it to connect to your ISP.
- Ensure that your devices are not performing background downloads. For example, if you have an Xbox or Playstation that’s always switched on, you may notice your latency spike when it begins to perform game updates in the background, especially if you don’t have a fibre broadband connection with lots of spare bandwidth. The same can be true of automatic app updates on your phone, so it’s a good idea to disable those as well.
- Change your Wi-Fi password. In this day and age, it’s unlikely that your neighbours have guessed your password and are stealing your Wi-Fi, causing latency spikes from bandwidth usage. However, it’s technically possible, so it’s worth changing to a more secure Wi-Fi password, just in case.
- Avoid using any applications or programs that could interfere with your web traffic. For example, VPN apps, or extremely strict firewall programs. Of course, it’s important to use antivirus software and firewalls, but using software that is so aggressive that it causes latency issues is generally not necessary.
- Contact your broadband provider and see if they have any suggestions to improve your ping rate. It could be that you have the wrong type of DSL filter, or an outdated router, that is causing the issue. However, some broadband providers are more helpful than others when it comes to providing this type of customer service.
- Upgrade to a faster broadband connection, if possible. This is especially likely to be useful if you notice that latency increases when other people get online. Fast fibre broadband can help you to get a low latency.
- If you’ve tried everything you can, and you believe that your ISP could be causing the issue, try to switch providers. Even if you can’t get a faster plan, another ISP might be more helpful in fixing your latency issue.
Which British broadband providers have the lowest latency?
Each year, Ofcom performs an in-depth study into the speeds and latency of every British ISP. They test the real-world performance of each broadband provider, using a sample of different internet connections.
As of the latest report, BT Full Fibre broadband has the lowest latency, with an average ping of 6.4-6.9ms. This includes their 300Mbps, 145Mbps, and 67Mbps plans.
Cable broadband services such as Virgin Media typically had a higher average latency, of around 15ms, while TalkTalk, Plusnet, and EE’s 36Mbps packages had a ping rate of around 10-12ms.
The difference between a 6ms and a 15ms latency reading is indistinguishable for most online activities, including gaming.
Conclusion
You’ve reached the end of our guide to broadband latency, what it means, its interaction with broadband speed, and how to improve it.
Have any questions about your latency, and how to reduce it? Feel free to ask us in the comments below.
About the author

Tyler is the co-founder of Broadband Savvy. He has been helping people improve their broadband connectivity since 2018 by writing about fibre broadband and mobile broadband providers, as well as creating tutorials to help people improve their broadband speeds and Wi-Fi signal.
Tyler is responsible for the majority of buyer’s guides and broadband reviews published on Broadband Savvy. He has a wealth of experience testing and reviewing different broadband tariffs, including fibre internet plans, as well as 4G and 5G broadband deals. He is responsible for testing and evaluating Wi-Fi routers, performing speed and latency tests, and comparing the value for money of different broadband providers on the market in the UK.
Before co-founding Broadband Savvy, Tyler had a long history of tinkering with computers. He built his first PC at the age of 12, and since then, he’s become obsessed with all things networking and internet-related. He’s a massive gamer, loves Rocket League, and also plays Sunday League football.